Twist drills для чего
Twist drills для чего


Откройте возможности нейронного машинного перевода PROMT
PROMT.One (www.translate.ru) – бесплатный онлайн-переводчик на основе нейронных сетей (NMT) для азербайджанского, английского, арабского, греческого, иврита, испанского, итальянского, казахского, китайского, корейского, немецкого, португальского, русского, татарского, турецкого, туркменского, узбекского, украинского, финского, французского, эстонского и японского языков.
Изучайте времена и формы глаголов в английском, немецком, испанском, французском и русском языках в разделе Спряжение и склонение. Учите употребление слов и выражений в разных Контекстах. Мы собрали для вас миллионы примеров перевода на разные языки, которые помогут вам в изучении иностранных языков и подготовке домашних заданий.
Переводите в любом месте и в любое время с помощью мобильного переводчика PROMT.One для iOS и Android. Попробуйте голосовой и фотоперевод, скачайте языковые пакеты для офлайн-перевода.
Поделиться переводом
Но сейчас вы можете переводить только 999 символов за один раз.
Пожалуйста, войдите или зарегистрируйтесь, чтобы переводить до 5 000 символов единовременно. войти / зарегистрироваться
Добавить в избранное
Для добавления в Избранное необходимо авторизоваться
twist drill
1 twist drill
2 twist drill
Тематики
3 twist drill
4 twist drill
5 twist drill
6 twist-drill
7 twist drill
8 twist drill
9 twist-drill
10 twist drill
11 twist drill
12 twist drill
13 twist drill
14 twist drill
15 twist drill
16 twist-drill
17 twist drill
18 twist drill
19 twist drill
20 twist drill
См. также в других словарях:
Twist drill — Twist Twist, n. 1. The act of twisting; a contortion; a flexure; a convolution; a bending. [1913 Webster] Not the least turn or twist in the fibers of any one animal which does not render them more proper for that particular animal s way of life… … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
twist drill — n. a kind of drill with deep helical grooves for carrying out chips and shavings … English World dictionary
twist drill — noun a bit or drill having deep helical grooves • Syn: ↑twist bit • Hypernyms: ↑bit * * * noun : a drill having one or usually two deep helical grooves extending from the point to the smooth portion of the shank * * * Mach. a drill with one or… … Useful english dictionary
twist drill — /ˈtwɪst drɪl/ (say twist dril) noun a drill with one or more deep spiral grooves in the body … Australian-English dictionary
twist drill — noun A rotating cutting tool, used for cutting holes in metal, wood, or other materials, that consists of an essentially conical point, relieved and fluted to form cutting lips, and spiral flutes which direct the chips away from the lips and… … Wiktionary
twist drill — noun Date: circa 1875 a drill having deep helical grooves extending from the point to the smooth portion of the shank … New Collegiate Dictionary
twist drill — Mach. a drill with one or more deep helical grooves in the body. [1870 75] * * * … Universalium
twist drill — A drill with a straight shaft incised with spiral cutting edges for boring a hole. Also see wood … Glossary of Art Terms
twist drill — A metal cutting drill with spiral flutes (grooves) to permit the exit of chips while cutting … Dictionary of automotive terms
Drill bit sizes — Drill bits are the cutting tools of drilling machines. They can be made in any size to order, but standards organizations have defined sets of sizes that are produced routinely by drill bit manufacturers and stocked by distributors. In the U.S.,… … Wikipedia
Twist — Twist, n. 1. The act of twisting; a contortion; a flexure; a convolution; a bending. [1913 Webster] Not the least turn or twist in the fibers of any one animal which does not render them more proper for that particular animal s way of life than… … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
twist-drill
1 twist drill
2 twist drill
Тематики
3 twist drill
4 twist drill
5 twist drill
6 twist-drill
7 twist drill
8 twist drill
9 twist-drill
10 twist drill
11 twist drill
12 twist drill
13 twist drill
14 twist drill
15 twist drill
16 twist-drill
17 twist drill
18 twist drill
19 twist drill
20 twist drill
См. также в других словарях:
Twist drill — Twist Twist, n. 1. The act of twisting; a contortion; a flexure; a convolution; a bending. [1913 Webster] Not the least turn or twist in the fibers of any one animal which does not render them more proper for that particular animal s way of life… … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
twist drill — n. a kind of drill with deep helical grooves for carrying out chips and shavings … English World dictionary
twist drill — noun a bit or drill having deep helical grooves • Syn: ↑twist bit • Hypernyms: ↑bit * * * noun : a drill having one or usually two deep helical grooves extending from the point to the smooth portion of the shank * * * Mach. a drill with one or… … Useful english dictionary
twist drill — /ˈtwɪst drɪl/ (say twist dril) noun a drill with one or more deep spiral grooves in the body … Australian-English dictionary
twist drill — noun A rotating cutting tool, used for cutting holes in metal, wood, or other materials, that consists of an essentially conical point, relieved and fluted to form cutting lips, and spiral flutes which direct the chips away from the lips and… … Wiktionary
twist drill — noun Date: circa 1875 a drill having deep helical grooves extending from the point to the smooth portion of the shank … New Collegiate Dictionary
twist drill — Mach. a drill with one or more deep helical grooves in the body. [1870 75] * * * … Universalium
twist drill — A drill with a straight shaft incised with spiral cutting edges for boring a hole. Also see wood … Glossary of Art Terms
twist drill — A metal cutting drill with spiral flutes (grooves) to permit the exit of chips while cutting … Dictionary of automotive terms
Drill bit sizes — Drill bits are the cutting tools of drilling machines. They can be made in any size to order, but standards organizations have defined sets of sizes that are produced routinely by drill bit manufacturers and stocked by distributors. In the U.S.,… … Wikipedia
Twist — Twist, n. 1. The act of twisting; a contortion; a flexure; a convolution; a bending. [1913 Webster] Not the least turn or twist in the fibers of any one animal which does not render them more proper for that particular animal s way of life than… … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
What is a Twist Drill Bit?
Take a closer look at the most widely used of all drill bit types.
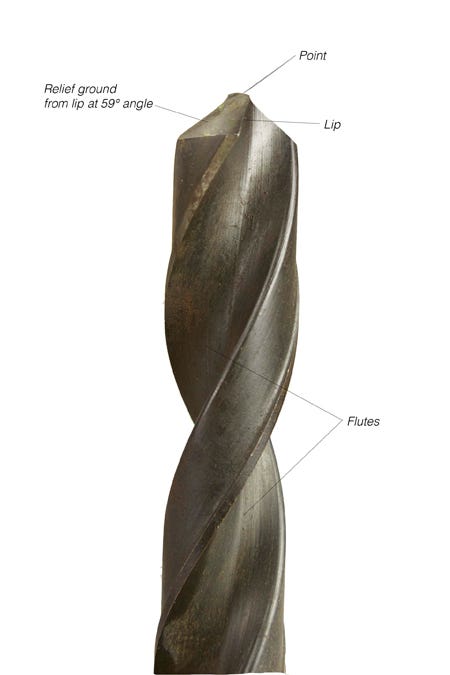
Twist drills (also commonly referred to as twist bits) are the most widely used of all drill bit types; they will cut anything from wood and plastic to steel and concrete. They are most frequently used for metal cutting, so they are generally made from M2 high-speed steel. At diameters up to about 1/2″, twist drills are not only the cheapest of all bits a woodworker could use, they offer the widest selection of sizes. Although they are designed for cutting metal, they will work quite well in wood, if sharp. This generally means that they have not been used to cut hard materials such as steel.
A twist drill is a metal rod of a specific diameter that has two, three or four spiral flutes running most of its length. Two-flute drills are for primary drilling, whereas three- and four-flute drills are only for enlarging cast or punched holes in a production situation. The section between the two flutes is called the web, and a point is formed by relief grinding the web to an angle of 59° from the drill’s axis, which is 118° inclusive. This forms a sloped cutting edge at the edge of the flute, which is called the lip. A twist drill is very inefficient at the point because the web leaves scant exit space for debris (called swarf) and because the point has a low surface speed compared to the periphery. For this reason, a good scheme for drilling larger holes is to first drill 1/4″ or less and then follow with the drill of the desired diameter.
In addition to creating the cutting lips, the flutes provide a place for the swarf to be drawn out of the hole. The spiral expedites this, but the flute becoming impacted with swarf is always a niggling problem. For this reason, a twist drill must be constantly cleared; that is, completely withdrawn from the hole. If you do this frequently, the swarf will be flung away, but if you wait too long, you will have to stop the drill and manually clean the flutes. Clearing is much easier with a drill press than with a drill motor. Wood is a poster child for quickly impacting a twist drill, so even more frequent clearing than with metal is necessary. This problem can be somewhat ameliorated by now and then applying wax or spraying silicone to the drill.


Normal length drills, such as come in the average assortment, are called jobber length. If a longer drill is needed, a good hardware shop will offer an aircraft or extra-length drill. If a shorter twist drill is desired, it is referred to as a screw-machine drill. Twist drills are offered in solid carbide and carbide-tipped as well. Carbide-tipped is the choice for drilling concrete.

Twist drills are difficult for users to sharpen. Great lengths are taken during manufacturing to have the lips at the same vertical height and angle. If the resulting point is not perfectly centered, and each lip does not cut a chip of equal width and thickness, the drill will wander and you will end up with an oversize hole that may not be straight either. While a skilled machinist can sharpen a twist drill by eye on a bench grinder, it will only do non-critical work thereafter! Only a drill sharpening jig or a dedicated machine will restore, new out of the box, accuracy to a dull drill.

The attack angle of a twist drill is controlled by the rate of twist of the flute. Drills are generally manufactured for cutting steel, which happily works out well for wood as well. This is far too aggressive for nonferrous metals such as brass and copper, which like a 5° negative rake angle. Breakout as the drill exits the material on the far side is particularly troublesome and commonly results in the workpiece spinning on the drill press table or the drill motor spinning in the operator’s hands. Either can result in severe injury. This dangerous situation can be almost completely overcome by creating a small flat on the lip that is parallel to the axis of the drill. Called lipping, it turns a unpredictable beast into a gentle pussy cat. What you are doing is effectively changing the rake angle of the drill to 0° instead of 15° positive. The flat does not have to be big, (1/64″ or less). The downside of lipping is that the drill will no longer drill steel unless you sharpen the point sufficiently to remove the flat. If you only own one set of drills, that is good reason to keep the lipping flat no larger than necessary.
Plenty of speed is the order of the day when drilling wood. You can use up to 3000 RPM for drills 1/4″ and smaller. Speed charts are readily available and it is good to have one on the shop wall. Center punching is a must if you want accurate hole location.
Twist drill краниостомия при хронических СДГ
Считается, что при этом методе происходит более медленная декомпрессия мозга и удается избежать резких колебаний давления, что бывает при использовании других методов и может приводить к осложнениям (например, паренхиматозное кровоизлияние). Это вмешательство можно осуществить под местной анестезией непосредственно у постели больного.
<Производят разрез кожи 0,5 см в проекции края гематомы, затем под углом в 45° к поверхности черепа делают отверстие тонким сверлом в направлении длинной оси гематомы. Если сверло не прошло через ТМО, то ее прокалывают спинальной иглой 18 Ga.>В субдуральное пространство устанавливают вентрикулярный катетер, который подсоединяют к мешку из комплекта для стандартной вентрикулостомии, который вешают на 20 см ниже краниостомического отверстия 179-181 (см. ниже Субдуральный дренаж). Пациент должен соблюдать ПР (см. выше). Адекватность дренажа оценивают по повторным КТ. Дренаж удаляют после того, как эвакуировано по крайней мере ≈20% жидкости и при улучшении состояния пациента, что может произойти в сроки от 1 до 7 д (в среднем 2,1 д).
Фрезевые отверстия при хронической СДГ
Во избежании повторного образования СДГ не следует делать маленькие фрезевые отверстия (если не используется субдуральный дренаж). В подвисочной области делают большое, Ø>2,5 см отверстие (рекомендуется его точно измерить). С помощью биполярной коагуляции сморщивают края ТМО и наружного листка капсулы гематомы до границ костного отверстия (не следует пытаться разделить эти слои, т.к. это может привести к кровотечению). Это обеспечивает постоянный отток жидкости, которая резорбируется височной мышцей. Отверстие можно прикрыть кусочком Gelfoam®, чтобы предотвратить просачивание свежей крови в трепанационное отверстие.
Субдуральный дренаж
После операции больной должен находиться в горизонтальном положении (см. выше). С профилактической целью можно назначить антибиотики на ≈24-48 ч после удаления дренажа, за это время больного постепенно переводят в возвышенное положение. Для того, чтобы иметь сравнительную информацию на случай ухудшения состояния, следует произвести КТ перед удалением дренажа (или вскоре после его удаления).
Исходы
Осложнения хирургического лечения
Хотя сами хронические СДГ часто являются практически бессимптомными, при их лечении возможны очень серьезные осложнения:
1. припадки (в частности не купирующийся эпилептический статус)
3. неспособность мозга расправиться и/или повторное накопление жидкости в субдуральном пространстве
4. напряженная пневмоцефалия: см. с.658
5. субдуральная эмпиема: может наблюдаться и у неоперированных больных 213
24.7.3. Спонтанная субдуральная гематома
Факторы риска, указанные в обзоре 21 случая, обнаруженных в литературе:
· АД: было в 7 случаях
· сосудистые аномалии: АВМ, АА 218
· инфекции: включая менингит, ТБ
· гиповитаминоз: особенно дефицит витамина С 219
· коагулопатии: включая иатрогенные (противосвертывающая терапия)
· внешне малозначимые воздействия (напр., переразгибание) или повреждения в результате непрямой травмы головы (напр., хлыстовые повреждения)
Источник кровотечения был установлен в 14 из 21 случаев. Во всех случаях это была артерия, обычно одна из ветвей СМА в области Сильвиевой щели. По одной из гипотез повреждение сосуда при минимальном травматическом воздействии происходит в месте арахноидальных спаек, образовавшихся в результате предшествующего воспалительного процесса.
Хирургическое удаление является методом выбора. При подострой или хронической СДГ достаточным может быть удаление через фрезевые отверстия (см. выше).
Травматическая субдуральная гигрома
Гигромы отличаются от хронических СДГ, при которых обычно имеется прилежащий очаг УГМ, а содержимым является жидкость бурого цвета (цвета «машинного масла»), иногда с темными сгустками, и может наблюдаться формирование капсулы, прилежащей к внутренней поверхности ТМО (гигромы не имеют капсулы).
«Осложненная гигрома» – сочетание гигромы со значительной СДГ, ЭДГ или ВМГ.
На КТ плотность жидкости соответствует плотности ЦСЖ.
Патогенез
Гигромы формируются вероятно в результате разрывов арахноидальной мембраны с истечением ЦСЖ в субдуральное пространство. Жидкость гигромы содержит преальбумин, который также обнаруживается в ЦСЖ, но отсутствует в СДГ. Разрывы арахноидальной оболочки наиболее часто происходят в области сильвиевой щели или хиазмальной цистерны. Другим возможным механизмом формирования гигром является постменингитное пропотевание (особенно после гриппозного менингита).
Жидкость может быть под высоким давлением. Гигрома может увеличиваться в размерах (возможен клапанный механизм) и вызывать масс-эффект, который может быть причиной существенных осложнений. У 19% пациентов с простыми гигромами были признаки атрофии ГМ.
Клинические проявления
Клинические проявления субдуральных гигром приведены в табл. 24-26. Во многих случаях очаговых симптомов не наблюдается. Осложененные гигромы обычно имеют более острые проявления и требуют более неотложного лечения.
Табл. 24-26. Основные клинические признаки травматических субдуральных гигром 220
| Тип гигромы | Простая | Осложненная | Всего |
| Кол-во пациентов | |||
| Спонтанное открывание глаз | 74% | 57% | 71% |
| Дезориентация или сопор | 65% | 57% | 64% |
| Изменения психического статуса без очаговых симптомов | 52% | 50% | 51% |
| Стабильный больной с неврологическим дефицитом или ухудшением | 42% | 7% | 36% |
| Припадки (чаще генерализованные) | 36% | 43% | 38% |
| Гемипарез | 32% | 21% | 30% |
| Ригидность мышц затылка | 26% | 14% | 24% |
| Анизокория (с сохранением реакции на свет) | 15% | 7% | 14% |
| Головная боль | 14% | 14% | |
| Без изменений умственного статуса | 8% | 0% | 6% |
| Гемиплегия | 6% | 14% | 8% |
| Кома (сохранена только реакция на боль) | 3% | 43% | 10% |
Лечение
Бессимптомные гигромы не требуют лечения. После простого дренирования через фрезевые отверстия часто наблюдаются рецидивы. Многие хирурги устанавливают субдуральный дренаж на 24-48 ч после операции. При рецидивировании может потребоваться или краниотомия с установлением места истечения ЦСЖ (может быть очень затруднительно) или установка субдурально-перитонеального шунта.
Исходы
По-видимому, исходы больше зависят от сопутствующих обстоятельств, чем от самой гигромы.
5 из 9 пациентов с осложнеными гигромами и субдуральными гематомами умерли. При простых гигромах осложнения наблюдались в 20% случаев (в 12% случаев при ¯ умственном статусе без очаговых симптомов и в 32% случаев при наличии гемипареза или гемиплегии).